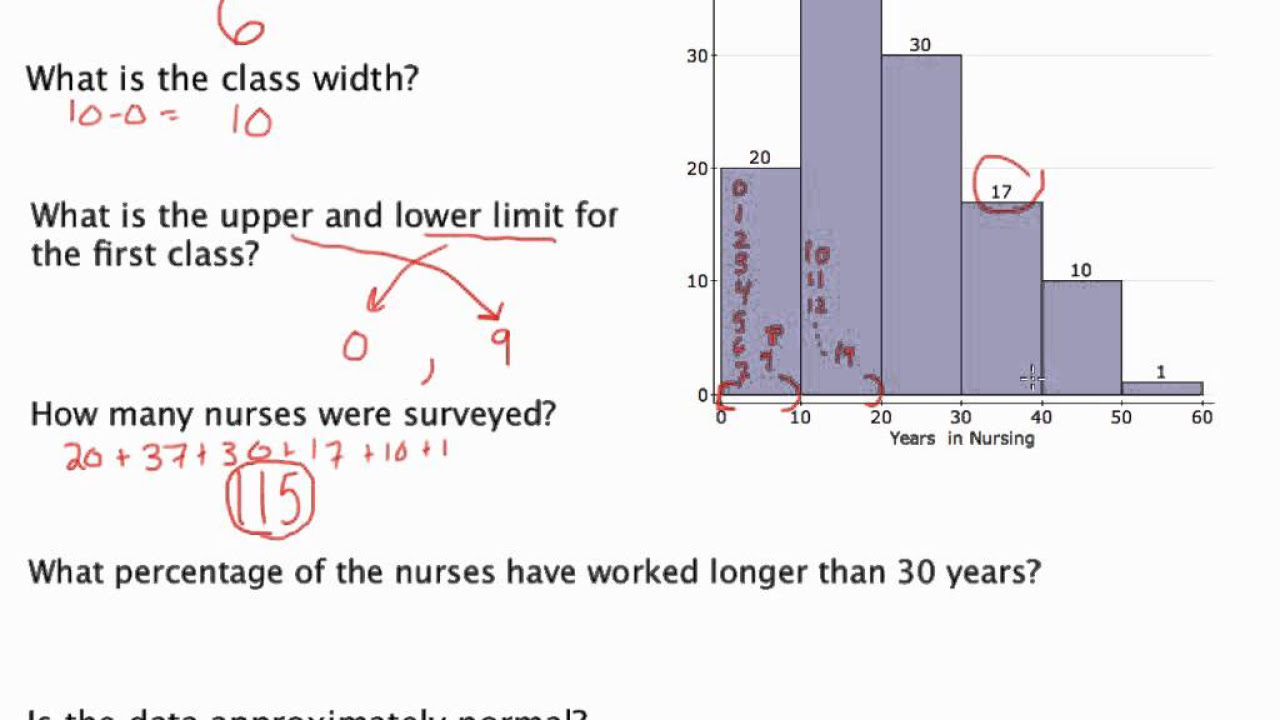
How to Read a Histogram: Effective Ways to Analyze Your Data in 2025
Understanding Histograms
Understanding histograms is fundamental for anyone involved in data analysis in today’s data-driven world. A **histogram** is a type of graphical data representation that enables quick interpretation of **frequency distributions**. It visualizes how data points are spread across different intervals or “bins”. Learning how to read a histogram effectively can unlock crucial insights from raw data, with possibilities for applications in research, education, or practical business solutions. This article offers a comprehensive approach to dissecting histograms, focusing on critical aspects like bin size selection, interpreting shapes, and distinguishing histograms from bar graphs.
Histogram Definition
A **histogram** is essentially a type of bar graph that displays data distribution by grouping data points into specified ranges, also referred to as bins. The height of each bar indicates the number of data points that fall within each bin, thus facilitating visual comprehension of frequency distribution. Understanding the key features of a histogram, such as its axes that generally denote bin ranges and counts, is pivotal for effective data interpretation. Moreover, a histogram provides a quick visual comparison between different datasets, making it invaluable for statisticians and analysts alike.
Frequency Distribution Graph
Frequency distribution graphs, particularly histograms, allow for effective visualization of data dispersion. By analyzing these graphs, one can assess how data clusters around particular values, revealing patterns that may not be immediately evident. A key advantage of using histograms over other graphical data representations is their ability to reveal the **shape and spread of data** more clearly, which is essential in identifying skewness, gaps, or clusters. Additionally, understanding the frequency distribution can assist in determining data trends that inform strategic decisions.
Analyzing Data Distributions
Analyzing data distributions through histograms can highlight how a dataset behaves. For example, examining a **normal distribution histogram** provides insights into how common the central tendency is in the data set, while identifying **outliers in histograms** can indicate potential errors or exceptions in the expected patterns. Armed with insights from histogram analysis, data analysts can refine their approaches, adapting their methods based on clearer visibility into the dataset. Appropriately utilizing the data from histograms can dramatically enhance the accuracy of interpretations made by the analyst.
Histogram Axes Explained
The structure of a histogram lends itself to effective data visualization, primarily through its well-defined axes. The x-axis typically represents the **bin ranges**, while the y-axis signifies the **frequency of occurrences** within those bins. Understanding these axes is crucial for reading and interpreting histograms correctly. The way the bars are constructed and aligned gives feed on the underlying frequency distribution, allowing for deeper insights into the data’s characteristics.
Determining Histogram Range
Determining the right range for the histogram is essential for accurate data representation. A histogram with a**poorly chosen range** can obscure valuable messages underlying the data. The range chosen should reflect the entire dataset, ensuring it encompasses all relevant observations without introducing unnecessary clutter. When choosing a range, consider factors such as the distribution type and the purpose of the analysis; a correctly defined range fosters more effective comparisons.
Bin Size Selection
Another critical aspect of effective histogram reading is **bin size selection**. Bins that are too wide can conceal the **data distribution’s true nature**, potentially leading analysts to overlook essential insights. Conversely, bins that are too narrow may indicate irrelevant fluctuations in the data. Striking the right balance during bin size selection is key to ensuring that the histogram remains both informative and interpretable, accentuating relevant data trends instead of rendering them ineffective. Tools and software for histogram creation often provide niched default settings, yet it’s essential to customize settings to adapt to specific datasets.
Histogram Communication Techniques
Effective histogram communication entails not just analyzing but presenting the information clearly. Using storytelling techniques to correlate visual data and utilize **histograms for effective communication** can significantly enhance understanding. Key to this is ensuring labels are clear, and are explicatively correlating data patterns with textual interpretations. This involves highlighting significant histogram features like peaks, tails, and the overall shape of the distribution. Keeping the audience in mind while interpreting histograms, so they can connect better with the insights provided, strengthens the communication efficacy.
Comparing Histograms Between Datasets
When dealing with multiple datasets, **comparing histograms** offers an excellent route for understanding changes or differences over time. This comparative analysis provides the opportunity to visually assess how a dataset evolves, helping to highlight shifts or anomalies that warrant further investigation. By reading data from histograms comparatively, analysts can observe trends, identify disparities, and make data-driven decisions more confidently.
Cumulative Histograms
Cumulative histograms offer a layered approach to data interpretation, instead of merely observing the frequency per interval. With cumulative histograms, each bin adds its frequency to the previous ones, forming an overall total that beautifully illustrates the data accumulation. This aids in spotting trends in **data visualization techniques** and helps to identify where most of the data resides. Utilizing cumulative histograms can ensure analysts fully grasp data movement, which is pivotal when planning strategic decisions.
Histograms and Real-World Applications
The utility of histograms transcends theoretical statistics and finds significant applications in various real-world scenarios. Industries like finance for analyzing market trends, healthcare for patient statistics, and education for standardized test scores heavily rely on **histogram analysis in research** for interpreting vast datasets. Moreover, histograms help facilitate improvements when assessing business processes, guiding teams to enhance operations based on established data trends. The application of these tools underlines their importance in fostering an accurate understanding of comprehensive data distributions.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding histograms is crucial for data visualization and analysis.
- Proper bin size selection and range determination significantly affect histogram utility.
- Cumulative histograms provide deeper insights into data patterns by demonstrating accumulation.
- Histograms serve various applications across standards in finance, healthcare, and educational assessments.
- Effective communication of histogram insights can enhance comprehension among diverse audiences.
FAQ
1. What are the common mistakes in histogram reading?
Common mistakes include misinterpreting bin sizes that can oversimplify or exaggerate data trends, as well as not accounting for data outliers which could mislead the analysis. Reading histograms without considering the overall distribution shape or neglecting the data range can also lead to erroneous conclusions in data interpretation.
2. How do I create a standard histogram?
Creating a standard histogram involves organizing your data into `bins`, counting the frequency of data points in each bin, and plotting these counts on the y-axis against the bins on the x-axis. Tools for creating histograms, both software and online platforms, streamline this process, ensuring that analysts can efficiently visualize their data distributions.
3. How can histograms reveal outliers?
Histograms can provide a visual identification of outliers through unusual spikes or limited frequency points segregated from the rest of the data distribution. Plotting data and observing the distribution allows analysts to spot observations that may deviate significantly from general trends, which can warrant deeper investigation or adjustments in analysis.
4. What are histogram storytelling techniques?
Histogram storytelling techniques involve presenting data trends clearly, emphasizing significant peaks, troughs, and shapes that correspond with narrative elements. Using visual aids that correlate data patterns enhances clarity and engagement, allowing the audience to connect better with the presented insights. This method transforms statistical findings into stories that communicate effectively.
5. Can histograms be used in sentiment analysis?
Yes, histograms can efficiently represent sentiment analysis results. By categorizing sentiment scores into bins based on their frequencies, analysts can visualize how sentiments are distributed across data sets, providing insightful narratives about public opinion or customer feedback.
6. How do cumulative histograms differ from regular histograms?
Cumulative histograms add the frequencies of each bin to represent a total frequency up to a certain point. This contrasts with regular histograms, which display only the frequency for each individual bin, providing a more comprehensive view of data accumulation over the entire range.
7. What criteria should I use for bin width selection?
When selecting bin widths, consider assessing your data distribution to ensure bins are neither too broad, which can mask important details, nor too narrow, which can introduce excessive noise. Tools and visualization software often provide default settings based on the dataset but refining them based on actual data characteristics can enhance histogram accuracy.