How to Effectively Handle Negative Exponents
Understanding Negative Exponents
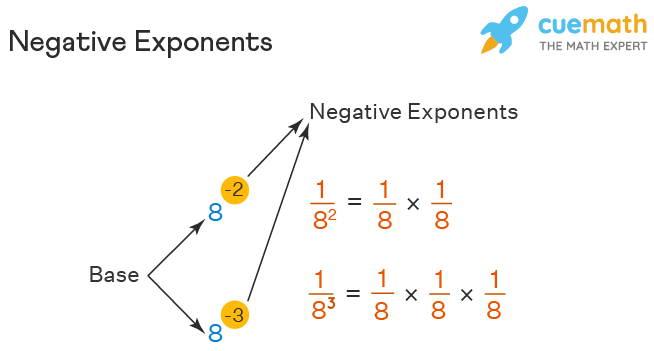
Negative exponents can be a challenging concept, but grasping the basics is essential for mastering the subject. **Understanding negative exponents** involves realizing that when a number has a negative exponent, it represents the reciprocal of that number raised to the corresponding positive exponent. For example, \( x^{-n} = \frac{1}{x^{n}} \). This definition is crucial in making sense of other operations that involve negative exponents, such as multiplying or dividing with them. By internalizing this fundamental rule, students can develop a clearer comprehension of how to calculate negative exponents in various mathematical situations.
Negative Exponent Rules
One of the first steps in **understanding negative exponents** is familiarization with the **negative exponent rules**. These rules dictate how exponents operate when they are negative. The primary rule states that a negative exponent indicates a reciprocal. Students should also be aware of the property which asserts that multiplying with negative exponents leads to considerations of both positive and negative bases. For example, when multiplying \( x^{-3} \times x^{5} \), the result would be \( x^{5-3} = x^{2} \), which combines both the positive and negative aspects of exponents. This foundational understanding is necessary for students looking to simplify negative exponents effectively.
Examples of Negative Exponents
To provide practical insight, let’s consider a few **negative exponent examples**. If we take \( 2^{-4} \), using the negative exponent rule, we simplify this to \( \frac{1}{2^{4}} = \frac{1}{16} \). Another example is \( 3^{-2} \), which translates into \( \frac{1}{9} \). These simple conversions can often resolve confusion around fractional outputs from negative exponents. Creating a **negative exponent worksheet** with challenges like these can assist in learning through practice. Exercises that incorporate various operations involving negative exponents help reinforce understanding and prepare learners for increasingly complex applications.
Simplifying Negative Exponents
Simplifying negative exponents effectively requires a clear understanding of the **properties of negative exponents**. This is crucial not just in algebraic contexts but also in practical mathematics where variables may carry negative powers. When faced with an expression like \( a^{-m} \times b^{-n} \), one may first convert those to their positive equivalents, resulting in \( \frac{b^{n}}{a^{m}} \). This inversion not only simplifies calculations but also aids in clearer graphing and function interpretations.
Negative Exponent Applications
**Applications of negative exponents** extend far beyond the classroom. For instance, scientific notation often employs negative exponents to express very small numbers succinctly, like \( 6.02 \times 10^{-23} \) for Avogadro’s number in chemistry. Furthermore, negative exponents can naturally occur in various equations across physics, such as expressing decay rates with exponential functions. Understanding these real-world applications can make learning more engaging and impactful, motivating students to delve deeper into the subject.
Teaching Negative Exponents
Effective techniques in **teaching negative exponents** involve multiple approaches. Using visual aids such as graphs to demonstrate how negative exponents behave in functions can help students visualize the concepts better. Interactive lessons where learners manipulate expressions with **negative exponents** can also prove beneficial. Ensuring students engage with **negative exponent exercises** and solving problems collaboratively can enhance understanding and retention, making the learning process dynamic.
Graphing Negative Exponents
Graphing equations that include **negative exponents** is instrumental in further imprinting the concept in a learner’s mind. The representation of functions like \( f(x) = x^{-1} \) reveals an asymptotic behavior which emphasizes the property of inverses in negative exponent calculations. The various shapes created by these functions illustrate the diminishing returns associated with negative exponentiation. Understanding how to graph these functions is essential for recognizing how they behave and interact within a larger context of mathematics.
Visualizing Negative Exponents
Utilizing visual tools can aid significantly in **visualizing negative exponents**. For example, plotting \( y = x^{-2} \) on a graph reveals how it approaches zero without ever touching it as \( x \) increases. This behavior is common for negative exponents and can connect students’ understanding between numerical concepts and their graphical representations. Using technology tools like graphing calculators, students can explore negative exponents across a range of values, developing an intuitive feel for how they function.
Real-life Applications of Negative Exponents
Exploring **real-world examples of negative exponents** can solidify students’ grasp of the topic. In finance, exponential decay models can use negative exponents to predict depreciation of assets over time. Similarly, in biology, equations may involve negative exponents to represent population decline or growth under specific environmental factors. Understanding these practical implications not only underscores the importance of negative exponents but also galvanizes student awareness of mathematics’ role in everyday life.
Key Takeaways
- Negative exponents indicate the reciprocal of a base raised to the corresponding positive exponent.
- Mastering the negative exponent rules is crucial for simplifying calculations and expressions.
- Real-world applications further illustrate their significance in fields like science and finance.
- Utilizing visual aids and interactive lessons enhances understanding and retention of negative exponent concepts.
FAQ
1. What is a negative exponent?
A **negative exponent** indicates that the base should be taken reciprocally. In mathematical terms, \( b^{-n} = \frac{1}{b^{n}} \), conveying that it expresses a relationship that often appears in algebraic manipulations and real-life applications.
2. How can I multiply numbers with negative exponents?
When multiplying with negative exponents, it’s essential to recall that the product rule applies. For instance, if you multiply \( a^{-m} \) and \( a^{-n} \), you can rewrite it as \( a^{-m-n} \), effectively combining the exponents while adhering to their original signs and properties.
3. Can you explain converting negative exponents?
**Converting negative exponents** primarily involves using the reciprocal rule: Change from \( x^{-n} \) to \( \frac{1}{x^{n}} \). This step is foundational in simplifying algebraic expressions involving negative powers.
4. What are common errors with negative exponents?
Common errors include neglecting to change the sign of the exponent during conversions or failing to apply the rules consistently across differing operations (e.g., addition vs. subtraction of exponents). Developing a meticulous approach can alleviate confusion over their properties.
5. How do teach negative exponents effectively?
Effective **teaching strategies for negative exponents** might include using interactive lessons, visual representations, and problem-solving exercises that allow students to collaborate and engage with the material, promoting a deeper understanding of negative exponent rules and applications.